Understanding Snake Infectious Stomatitis: A Guide for Reptile Enthusiasts
Overview of snake infectious stomatitis
Snakes, with their mesmerizing beauty and unique charm, have captivated the hearts of reptile enthusiasts for centuries. These fascinating creatures come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each with its own set of characteristics and care requirements. However, just like any other living being, snakes are susceptible to various health conditions that can affect their well-being. One such condition that reptile enthusiasts should be aware of is snake infectious stomatitis.
Snake infectious stomatitis, also known as mouth rot, is a distressing ailment that primarily affects the oral cavity of snakes. It is characterized by inflammation and infection of the mucous membranes lining the snake’s mouth, leading to a range of symptoms and potential complications if left untreated. Understanding this condition and its implications is crucial for snake owners, as early detection and appropriate management can make a significant difference in the snake’s overall health and quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the depths of snake infectious stomatitis, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and frequently asked questions. By the end of this article, you will have a well-rounded understanding of this condition, equipping you with the knowledge to provide the best care for your scaly companions.
So, let us embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries of snake infectious stomatitis and discover the steps we can take to ensure the well-being of our beloved snakes.
What is Snake Infectious Stomatitis?
Definition and Causes
Snake Infectious Stomatitis, also known as mouth rot or Infectious Stomatitis, is a common and highly contagious infection that affects snakes. This condition primarily affects the oral cavity and the surrounding tissues, causing inflammation and ulcers. While it can occur in various species of snakes, it is particularly prevalent in captive reptiles.
The causes of Snake Infectious Stomatitis can vary, but the most common culprit is poor husbandry practices. Inadequate sanitation, improper temperature and humidity levels, and unsanitary living conditions can create an environment conducive to the growth and spread of bacteria. Additionally, poor nutrition and stress can weaken a snake’s immune system, making them more susceptible to infections.
It is important to note that Snake Infectious Stomatitis is not the only oral infection that snakes can experience. Other conditions, such as snake scale rot and snake mouth rot, can also manifest with similar symptoms. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a veterinarian for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
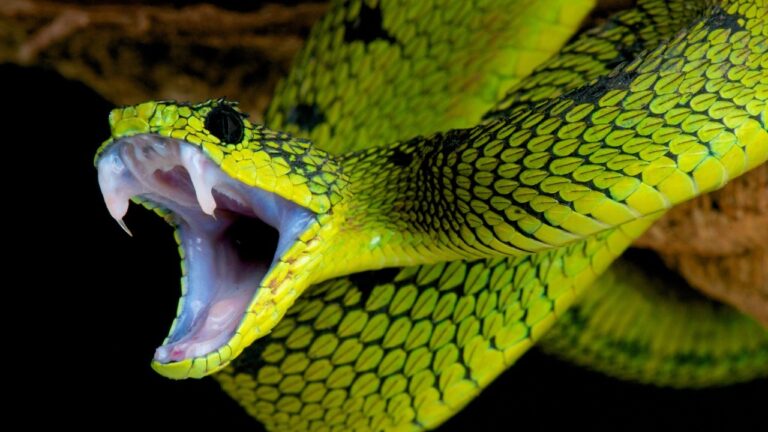
Symptoms and Signs
Identifying the symptoms and signs of Snake Infectious Stomatitis is crucial for prompt detection and treatment. The infection typically starts in the mouth and can progress to affect other areas of the snake’s body if left untreated.
Common symptoms and signs of Snake Infectious Stomatitis include:
- Loss of appetite: Infected snakes may show a decreased interest in food or refuse to eat altogether.
- Swollen or discolored gums: The gums may appear red, swollen, or exhibit a yellowish tint.
- Excessive saliva: Snakes with Infectious Stomatitis may exhibit an increase in saliva production, leading to drooling or excessive foaming around the mouth.
- Ulcers and lesions: The mouth may have open sores or lesions, which can be painful for the snake and may lead to difficulty in eating or swallowing.
- Foul odor: Infected snakes may emit a foul odor from their mouth due to the presence of bacteria.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your snake, it is crucial to seek veterinary attention immediately. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications.
In the next section, we will explore the diagnostic methods used by veterinarians to identify Snake Infectious Stomatitis and discuss the available treatment options. Stay tuned!
Note: If you’re interested in learning more about other common snake health issues, such as snake mites treatment or snake shedding problems, be sure to check out our informative articles on SerpentSuppers.com.
Diagnosing Snake Infectious Stomatitis
When it comes to diagnosing snake infectious stomatitis, a comprehensive veterinary examination is crucial. Veterinarians who specialize in reptiles have the expertise and knowledge to accurately diagnose and treat this condition. They will carefully assess the snake’s overall health and examine its oral cavity for any signs of infection.
During the veterinary examination, the veterinarian will look for symptoms such as swollen gums, excessive saliva, ulcers, or discoloration in the snake’s mouth. They may also check for any abnormalities in the snake’s jaw or head. It is important to note that these symptoms can sometimes resemble other reptile mouth disorders, such as snake mouth rot or snake scale rot. Therefore, a thorough examination is necessary to differentiate between these conditions.
In addition to the physical examination, swab tests and laboratory analysis play a significant role in diagnosing snake infectious stomatitis. The veterinarian will carefully collect a swab sample from the affected areas within the snake’s mouth. This sample will then be sent to a laboratory for further analysis.
The laboratory analysis involves examining the swab sample under a microscope to identify the presence of bacteria, viruses, or fungi that may be causing the infection. This analysis helps to confirm the diagnosis of snake infectious stomatitis and rule out other potential diseases or conditions.
It is worth mentioning that snake infectious stomatitis can sometimes be challenging to diagnose, especially in its early stages. Therefore, it is important to consult with a qualified veterinarian who has experience in reptile medicine. Their expertise and access to specialized laboratory testing will greatly aid in the accurate diagnosis of this condition.
In the next section, we will explore the various treatment and management options available for snake infectious stomatitis. Stay tuned!
For more information on related snake health issues, you can read our articles on snake inclusion body disease and snake respiratory infection.
Treatment and Management
When it comes to treating snake infectious stomatitis, a multi-faceted approach is essential. The goal is to alleviate the symptoms, eliminate the infection, and prevent further spread of the disease. This section will delve into the various treatment and management options available to reptile enthusiasts dealing with this challenging condition.
Medications and Antibiotics
One of the primary components of treating snake infectious stomatitis involves the use of medications and antibiotics. These powerful tools help combat the infection and aid in the recovery process. Common antibiotics such as enrofloxacin and doxycycline are often prescribed by veterinarians to target the bacteria responsible for the disease. These medications work by inhibiting bacterial growth and promoting healing.
It’s crucial to remember that medications should only be administered under the supervision of a qualified veterinarian. They will determine the appropriate dosage and duration of treatment based on the severity of the infection and the specific needs of the snake. Compliance with the prescribed treatment plan is vital to ensure a successful outcome.
Supportive Care
In addition to medications, providing supportive care plays a significant role in the management of snake infectious stomatitis. This involves creating an optimal environment for the snake’s recovery and supporting its overall well-being. Adequate hydration is crucial, as it helps flush out toxins and promotes healing. Offering fresh, clean water and monitoring the snake’s drinking habits are essential steps in providing the necessary support.
Moreover, maintaining proper humidity levels in the snake’s enclosure is crucial for preventing further complications and promoting healing. Dry conditions can exacerbate the symptoms, while excessive moisture can create an environment conducive to the growth of harmful bacteria. Striking the right balance is key, and regular monitoring of humidity levels using a hygrometer is highly recommended.
Quarantine and Isolation
To prevent the spread of snake infectious stomatitis to other reptiles, quarantine and isolation measures must be implemented. Isolating the infected snake from healthy individuals is crucial to avoid transmission of the disease. A separate enclosure should be designated for the affected snake, ideally in a different room or area to minimize the risk of contamination.
During the quarantine period, strict hygiene practices should be observed. This includes thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting the enclosure, accessories, and any equipment that comes into contact with the infected snake. Appropriate disinfectants recommended by a veterinarian should be used to ensure effective eradication of the bacteria.
It’s important to note that the duration of quarantine will vary depending on the severity of the infection and the snake’s response to treatment. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential to monitor progress and determine when it is safe to reintroduce the snake to its original enclosure or to interact with other reptiles.
By following these treatment and management strategies, reptile enthusiasts can effectively combat snake infectious stomatitis and provide their beloved snakes with the care they need to recover. Remember, early detection and prompt intervention are crucial for a successful outcome. Stay vigilant and consult with a reptile veterinarian for personalized guidance and support throughout the treatment process.
Preventing Snake Infectious Stomatitis
When it comes to the health and well-being of our scaly companions, prevention is always better than cure. Snake infectious stomatitis, also known as mouth rot, is a condition that can be avoided with proper care and attention. By implementing a few simple measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of your snake developing this uncomfortable and potentially dangerous infection.
Hygiene Practices
Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment is crucial for preventing snake infectious stomatitis. Regularly cleaning and disinfecting your snake’s enclosure will help eliminate any potential sources of infection. Thoroughly wash all surfaces, including the substrate, water dish, and any objects or hides within the enclosure, using a reptile-safe disinfectant. Ensure that the enclosure is completely dry before reintroducing your snake to its habitat.
Regularly removing feces and shed skin from the enclosure is also essential. Dispose of waste appropriately and clean any soiled areas promptly. Additionally, avoid handling your snake with dirty hands or using contaminated tools, as this can introduce harmful bacteria into their mouth and predispose them to infectious stomatitis.
Quarantine Procedures
Implementing quarantine procedures is an effective way to prevent the spread of infectious diseases among snakes. Whenever you bring a new snake into your collection, it is crucial to isolate them from your existing snakes for a period of time. This allows you to observe the new snake for any signs of infectious stomatitis or other illnesses before introducing them to the rest of your collection.
During the quarantine period, house the new snake in a separate enclosure with its own set of equipment and supplies. Avoid sharing items such as feeding tongs or water dishes between snakes, as this can facilitate the transmission of pathogens. Be diligent in monitoring the health of the quarantined snake, and consult a veterinarian if you notice any concerning symptoms or behaviors.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups are an essential part of maintaining your snake’s overall health and detecting any potential issues early on. Schedule annual or biannual visits with a qualified reptile veterinarian to ensure that your snake is in top condition. These professionals have the expertise to identify and address any underlying health concerns, including infectious stomatitis.
During these check-ups, the veterinarian will perform a thorough examination of your snake, paying special attention to the oral cavity. They may recommend swab tests or laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of infectious stomatitis or rule out other possible conditions. By catching the infection in its early stages, you can prevent it from progressing and causing further harm to your snake.
Remember, by following proper hygiene practices, implementing quarantine procedures, and scheduling regular veterinary check-ups, you can significantly reduce the risk of your snake developing infectious stomatitis. Take these preventive measures seriously, and your scaly friend will thank you with a lifetime of good health and happiness.
Internal links: snake scale rot, snake mouth rot
Frequently Asked Questions
Is snake infectious stomatitis contagious to humans?
Snake infectious stomatitis, also known as snake mouth rot, is a condition that primarily affects reptiles, including snakes. However, it is important to note that snake infectious stomatitis is not contagious to humans. While humans can contract certain infections from reptiles, such as salmonella, snake infectious stomatitis is not one of them. It is crucial to maintain proper hygiene practices when handling reptiles to minimize the risk of any potential infections.
If you have concerns about zoonotic diseases or other health risks associated with reptiles, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a veterinarian who specializes in exotic animals.
Can snake infectious stomatitis be prevented through vaccination?
Currently, there is no specific vaccination available to prevent snake infectious stomatitis. Vaccination against this condition is not yet a viable option. However, there are other important preventive measures that reptile enthusiasts can take to minimize the risk of their snakes developing this infection.
Maintaining good hygiene practices, including regular cleaning and disinfection of enclosures, is crucial. It is also important to provide appropriate temperature and humidity levels in the snake’s habitat to support their overall health and immune system.
What should I do if my snake is diagnosed with infectious stomatitis?
If your snake has been diagnosed with infectious stomatitis, it is essential to take immediate action to ensure their well-being and prevent the infection from spreading. Here are some key steps to follow:
-
Consult a reptile veterinarian: Seek professional guidance from a veterinarian who specializes in reptile care. They will provide a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your snake’s specific needs.
-
Follow the prescribed treatment: The veterinarian may prescribe medications, such as antibiotics, to combat the infection. It is crucial to administer the medications as directed and complete the full course of treatment.
-
Provide supportive care: Alongside the prescribed medications, supportive care is crucial for your snake’s recovery. This may include maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels in the enclosure, ensuring the snake stays hydrated, and providing appropriate nutrition.
-
Quarantine and isolation: To prevent the spread of infectious stomatitis to other snakes, it is essential to isolate the affected snake. Separate them from other reptiles and follow proper quarantine protocols until they have fully recovered.
-
Monitor and follow-up: Regularly monitor your snake’s progress and follow any post-treatment instructions provided by the veterinarian. If there are any concerns or if the symptoms persist, consult your veterinarian promptly.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are vital in managing snake infectious stomatitis effectively. With proper care and attention, most snakes can recover from this condition and regain their health.
For more information about snake health and other reptile-related topics, feel free to explore our blog, where we cover various health issues, such as snake scale rot, snake respiratory infection, and snake inclusion body disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding snake infectious stomatitis is crucial for reptile enthusiasts who want to ensure the health and well-being of their beloved snakes. This article has provided an in-depth overview of this condition, including its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies. By familiarizing yourself with the signs and symptoms of snake infectious stomatitis, you can take prompt action and seek veterinary attention if necessary.
Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are key to effectively managing snake infectious stomatitis. If you suspect that your snake may be suffering from this condition, it is important to consult a veterinarian who specializes in reptiles. They will conduct a thorough examination and may perform swab tests and laboratory analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for snake infectious stomatitis typically involves a combination of medications and antibiotics to combat the underlying infection. Additionally, providing supportive care, such as maintaining proper temperature and humidity levels, can help alleviate discomfort and aid in the healing process. Quarantine and isolation are also essential to prevent the spread of the infection to other snakes in your collection.
Prevention is always better than cure when it comes to snake infectious stomatitis. Practicing good hygiene, including regular cleaning and disinfection of enclosures, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Implementing quarantine procedures for new snakes before introducing them to your existing collection is another critical preventive measure. Regular veterinary check-ups can also help detect any potential health issues early on, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment.
While snake infectious stomatitis is not contagious to humans, it is essential to prioritize your own safety when handling infected snakes. Always practice proper hygiene and avoid direct contact with any open wounds or sores on the snake’s mouth. If you suspect your snake may have infectious stomatitis, it is best to consult a veterinarian rather than attempting to treat it yourself.
In conclusion, by staying informed about snake infectious stomatitis and taking proactive measures to prevent and manage this condition, reptile enthusiasts can ensure the well-being and longevity of their scaly companions. Remember that snake infectious stomatitis is just one of many potential health issues that snakes can face, so it is essential to stay vigilant and seek professional help whenever necessary.
For further information on other snake health issues, including snake scale rot, snake mouth rot, snake mites treatment, snake inclusion body disease, snake respiratory infection, snake septicemia, snake prolapse treatment, snake shedding problems, snake kidney disease, and snake neurological disorders, please visit SerpentSuppers.com where you can find comprehensive resources and expert advice to keep your snakes healthy and thriving.